Java Handy Resources
Published:
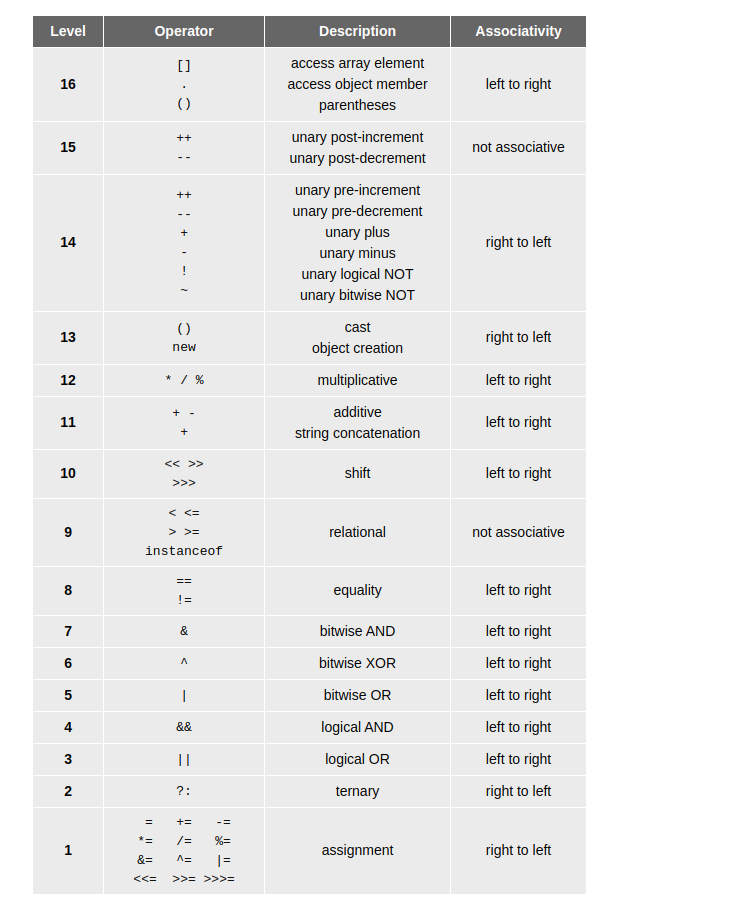
Operator Precedence
I forgot the precedence of Java operators frequently, so I paste it here from Sedgewick’s Algo site.
Java useful code snippets
Here is a collection of some useful Java code snippets from online. Paste it here for handy access.
/* Array */
Arrays.fill(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, int val)
Arrays.sort(nums, new Comparator<Point>() { @Override
public int compare(Point p1, Point p2) {
return p1.x - p2.x; // ascending based on p.x
} });
// pair: is pair[][], sort each row based on pair[i][0], ascending
Arrays.sort(pair, (a, b)->(a[0] - b[0]));
/* Special collection */
// the order of set.iterator().next() == the order put into the set
// typical use: when need to keep a set size k, and delete the oldest element,
// just need to delete set.iterator().next()
LinkedHashSet<Integer> set = new LinkedHashSet<>();
/* Deque/Queue */
Deque<Iterator<Integer>> deque = new LinkedList<>();
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>(); deque.offerFirst(num);
int num = deque.peekFirst();
int prev = deque.pollLast();
int cur = deque.peekLast();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(num);
int count = queue.poll();
queue.peek();
/* Stack */
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1); num = stack.pop();
/* PriorityQueue */
// the element of PQ can be Map.Entry: PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Character, Integer>> pq
= new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b.getValue() - a.getValue()); pq.addAll(map.entrySet());
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder()); pq.offer(5);
int m = pq.poll();
PriorityQueue<Tuple> pq = new PriorityQueue<Tuple>(); // And override compareTo function in Tuple class:
class Tuple implements Comparable<Tuple> {
int x;
int y;
int val;
//... @Override
public int compareTo(Tuple that) { return this.val - that.val;
} }
/* Map: */
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry:countMap.entrySet()) { // ...
}
for (int stop:routes[i]) { map.putIfAbsent(stop, new HashSet<>()); map.get(stop).add(i);
}
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
// need to return List<List<String>>:
// the type of map.values() is Collection<List<String>>, convertion is needed: return new ArrayList<List<String>>(map.values()); // convert
/* TreeMap/TreeSet: */
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.floorKey(num); map.ceilingKey(num); map.lowerKey(num);
// find the greatest key <= num // find the least key >= num
// find the greatest key < num
map.higherKey(num); // find the least key > num
// subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive, K toKey, boolean toInclusive)
// can be used in remove several map entries at the same time, eg: merge intervals map.subMap(start, true, end, false).clear();
// need to convert it as well:
public List<Integer> getValues() {
return new ArrayList<>(map.values()); }
TreeSet<Integer> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
Integer val = treeSet.ceiling(x); // find the least number >= x in treeSet
/* List */
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
// eg: create an List with {1,3,5}:
res.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[k])));
LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>(); res.removeFirst();
res.add(num);
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int index = Collections.binarySearch(list, num); // search for the index of num if (index < 0) index = -(index + 1); // not exist, index to insert in
list.set(idx, newNumber); list.addAll(list2);
list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[front], nums[i], nums[back])) list.addAll(Arrays.asList(1,2,3));
// Use list to create graph:
List<Integer>[] freqList = new ArrayList[nums.length + 1]; ArrayList[] graph = new ArrayList[numCourses];
return list.subList(0, k);
/* Iterator */
public class ZigzagIterator { Deque<Iterator<Integer>> deque;
public ZigzagIterator(List<Integer> v1, List<Integer> v2) { deque = new LinkedList<>();
if (v1 != null && !v1.isEmpty()) deque.offerLast(v1.iterator()); if (v2 != null && !v2.isEmpty()) deque.offerLast(v2.iterator());
}
public int next() {
Iterator<Integer> cur = deque.pollFirst(); int num = cur.next();
if (cur.hasNext()) deque.offerLast(cur);
return num; }
public boolean hasNext() { return !deque.isEmpty();
} }
public class NestedIterator implements Iterator<Integer> { Stack<NestedInteger> stack = new Stack<>(); @Override
public Integer next() {
return stack.pop().getInteger(); }
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
// ...
} }
Iterator<List<Integer>> listIter; Iterator<Integer> curIter;
public void functionExec(List<List<Integer>> vec) { listIter = vec.iterator();
if (listIter.hasNext()) {
curIter = listIter.next().iterator(); }
}
/* StringBuilder */
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
if (sb.length() > 0) sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1); sb.delete(int start, int end)
sb.append(str);
sb.toString();
sb.length();
sb.reverse(); sb.setLength(len); sb.insert(idx, str);
/* Collection change/convert */
// switch from a list to a set:
Set<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordList);
// change from List<String> to String[]:
List<String> words;
String[] wordlist = words.toArray(new String[words.size()]);
/* string */
//public static String join(CharSequence delimiter,
// Iterable<? extends CharSequence> elements) List<String> strings = new LinkedList<>();
// can use: Set<String> strings = new LinkedHashSet<>(); strings.add("Java");strings.add("is");
strings.add("cool");
String message = String.join("-", strings);
//message returned is: "Java-is-cool"
// String and int can concatenate directly: String s = 1 + "024"; // no problem
// but cannot connect directly with char: String s = '0' + "5"; // is not what expected
// search for a char from str1.substring(idx+1):
idx = str1.indexOf(s.charAt(i), idx+1);
s.startsWith(word, i) // == if s.substring(i).startsWith(word)
// Replace a substring in string:
!start.replace("X", "").equals(end.replace("X", ""))
str.toCharArray(); str.trim();
str = str.toLowerCase();
String numStr = String.valueOf(num); // int to string s1.compareTo(s2) < 0;
/* Character */
Character.isUpperCase(c); Character.isDigit(c); Character.isLetterOrDigit(c);
/* Math/Number */
n >>>= 1; // unsigned 无符号右移 n >>= 1; // signed
int sqrt = (int)Math.sqrt(n); // need to use (int) int pow = (int) Math.pow(2, height); // 2^height
(1 << bits); // same as Math.pow(2, bits-1);
Integer.bitCount(n); // count the # of bits that is 1 Integer.highestOneBit(n);
Integer.valueOf(numStr); // string to integer Integer.parseInt(numStr);
Random rand = new Random();
int randNum = rand.nextInt(size); // get a random int in [0, size) rand.nextDouble(); // random double of [0,1)
/* Great examples/usage */
// 500 in high freq-2:
public String[] findWords(String[] words) {
return Stream.of(words).filter(s -> s.toLowerCase().matches("[qwertyuiop]*|[asdfghjkl]*|[zxcvbnm]*")).toArray(String[]::new);
}
// time api:
import java.time.Instant;
Instant start = Instant.now();
Instant end = Instant.now();
long diff = Duration.between(start, end).toMillis();
// .toDays(), .toHours(), .toMinutes(), .toNanos(), .getSeconds() // .plusSeconds(), .plusMinutes()
// check if a char is a tab: charc='\t'; //cwouldbeTAB
// get all lines from a text file: // here used 4 ways to do it:
public static List<String> readAllLines1(File file) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file))) {
for (String line = reader.readLine();line != null;line = reader.readLine()) {
res.add(line); }
} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();
}
return res; }
// Files.newBufferedReader
public static List<String> readAllLines2(String fileName) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
try (BufferedReader br = Files.newBufferedReader(Paths.get(fileName))) {
br.lines().forEachOrdered(res::add); } catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }
return res; }
// Files.readAllLines
public static List<String> readAllLines3(String fileName) { List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
try {
res.addAll(Files.readAllLines(Paths.get(fileName))); } catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); }
return res; }
// scanner
public static List<String> readAllLines4(String fileName) { List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
try(Scanner input = new Scanner(Paths.get(fileName))) { while (input.hasNextLine()) {
res.add(input.nextLine()); }
} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();
}
return res; }

Leave a Comment